Types of e-health
e-health is a generic term that encompasses all healthcare-related applications, technologies and systems are encompassed, that result from the interaction of medicine, genetics and technologies. It uses appropriate technologies to engage the full spectrum of healthcare providers, consumers and researchers to deliver integrated, efficient and personalised care to patients and families.
The outcomes are:
- Improved quality of care.
- Easy access to health services.
- Reduction in the cost of health services.
- Better management of patient’s health (prevent diseases, be up to date with treatment options, etc.)
The main types of e-health are:
1. Electronic Health Record (EHR)
Collects electronic health information about a patient, which includes their medical history, medications and allergies, immunisation status, laboratory test results, radiographs, vital signs, personal statistics such as age and weight, progress notes and problem details.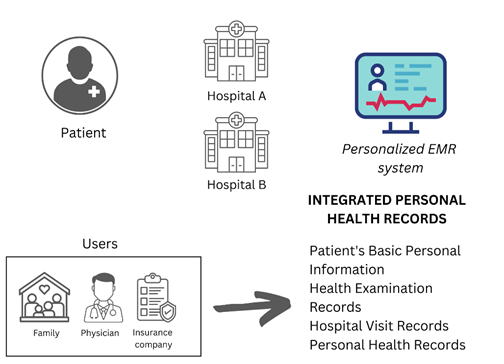
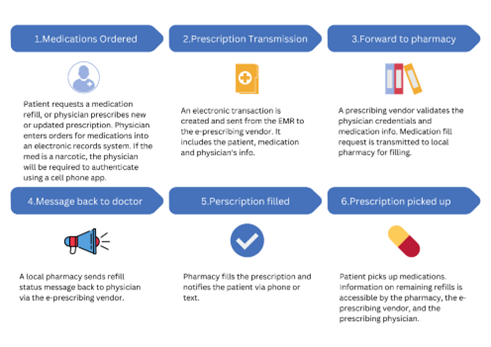
2. e-prescribing
Access to prescribing options, printing prescriptions to patients and sometimes electronic transmission of prescriptions from doctors to pharmacists.
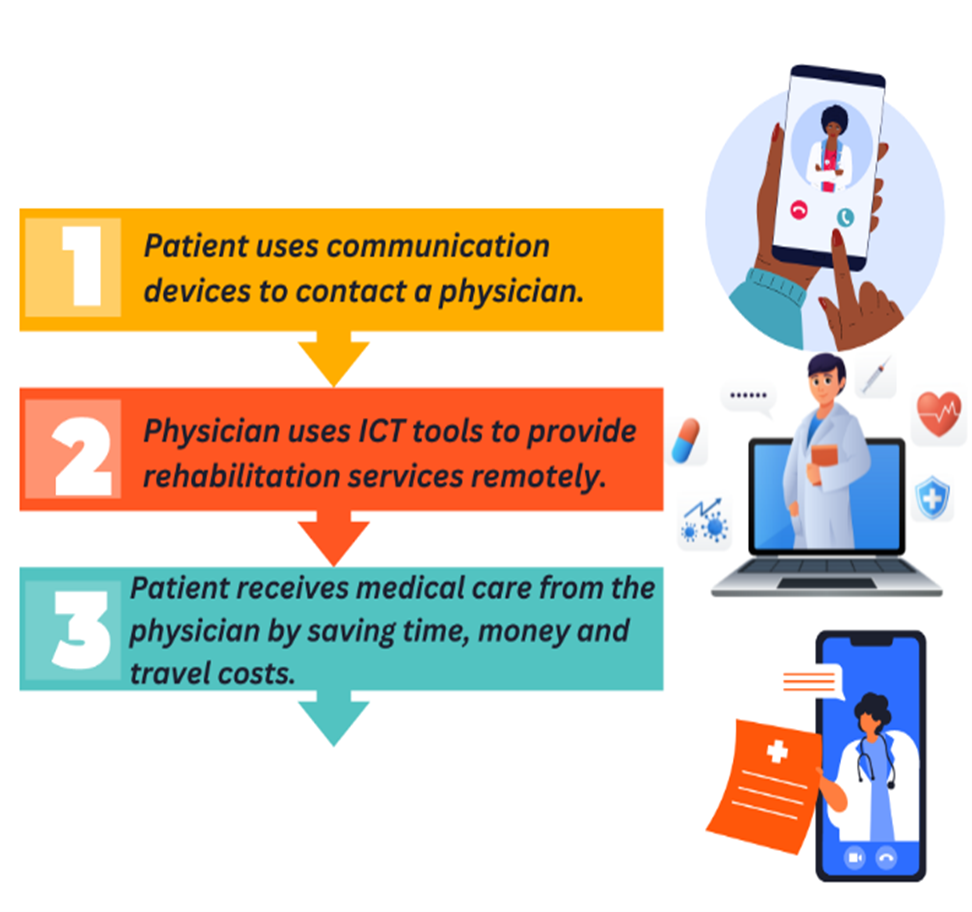
3. Telehealth, telemedicine & telerehabilitation
- Telemedicine is the remote physical and psychological diagnosis and treatment, including telemonitoring of patient data and video conferencing.
- Telerehabilitation is the use of information and communication technologies (ICT) to provide rehabilitation services to people remotely in their home or other environments, also known as, telecommunication (communication over a distance).
- Telehealth: people in remote areas with limited access to healthcare can get the medical care they need by saving time, money and travel costs for doctors and patients.
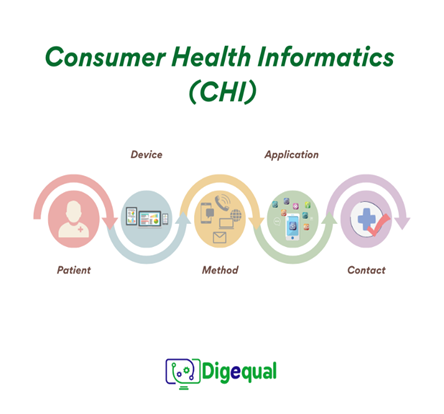
4. Consumer Health Informatics (CHI)
- Patients use electronic resources, i.e., Internet, as a research tool for condition and treatment information on medical topics in order to manage their health concerns. Thus, patients interact directly with the healthcare system online, without the presence of a healthcare professional.
- Patients can use devices, such as computers, mobile phones/tablets or any monitoring devices at home, by different methods, i.e., voice, SMS, Internet, emails, which are organized in an application way, in order to interact with health care providers (physicians, hospitals).
5. m-health
- The use of mobile devices, smartphones and portable electronic devices for health purposes.

6. Sensors and Wearable Devices
- Such devices allow continuous health monitoring and prevention at low cost. Sensors can be integrated into various accessories such as clothing, hats, wristbands, socks, shoes, glasses and other devices such as wristwatches, headphones and smartphones.
- In case of e-health devices, wearable technologies collect a very large amount of personal data, stored in cloud platforms, monitored by medical practitioners and trigger notifications in case of unusual data, i.e., heart attack, etc.

